Respiratory Infections
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

A study of pregnant women positive for COVID-19 at delivery found no evidence of vertical transmission, but increased gastrointestinal problems in their newborn infants.

A comparison of COVID-19 PCR tests and rapid self-tests found self-tests to be highly accurate and user-friendly for children.

The federal agency authorized the therapy as a standalone treatment via a revised EUA in July of last year.

Active immunization of pregnant women with investigational vaccine protected infants from RSV from birth through at least 6 months.
Investigators examined whether rapid antigen tests were less sensitive to variants of concern. Though the tests detected Omicron, all but 1 were less effective in detecting the Delta variant.
Investigators identify 11 crucial “protection-defining genes” that prevent a severe disease response to COVID-19 infection.

Medicago’s plant-based vaccine, Covifenz, was 69.5% effective against symptomatic COVID-19 infection and 78.8% effective against moderate-to-severe disease.

A Colorado person tested positive for avian influenza. The patient worked closely with poultry, their only symptom was fatigue, and they have since recovered after a few days.

Ensovibep, the COVID-19 antiviral treatment developed by Novartis and Molecular Partners, is facing delays in its quest for emergency authorization after the FDA indicated more study data is required.

Lasting 505 days, investigators documented the longest known COVID-19 infection. The research, presented at ECCMID, also found one of the first cases of occult COVID-19, in which a patient who tests negative is later found to have ongoing COVID-19.

A group of over 60 scientists participated in a communication to the federal agency to advocate for measuring these cells in COVID-19 vaccine trials.
Pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) hospitalizations were 41% lower than expected during the outbreak of COVID-19.
Investigators used procalcitonin (PCT) levels to guide antibiotic recommendations in pediatric intensive care units. PCT-guided antibiotic stewardship decreased the number of antibiotic days without leading to therapy failure.
What are the clinical characteristics of children under 1 year old who are hospitalized with COVID-19 infection?
One study, presented at the Critical Care Congress, found that initiating remdesivir (Veklury) earlier did not significantly reduce the recovery time of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
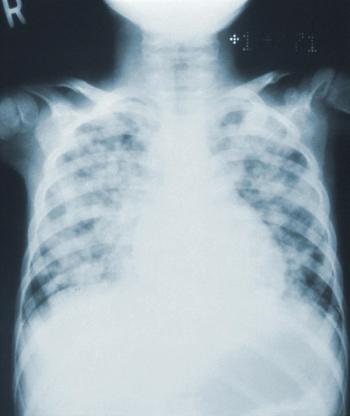
An analysis of readmissions after hospitalization with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in France found that few readmissions were avoidable, supporting criticism that the measure may lead to unfair penalties under pay-for-performance programs.

Antimicrobial stewardship efforts, such as education for healthcare providers, significantly decreased community-acquired pneumonia antibiotic prescriptions in COVID-19 patients.
Selecting initial antibiotic for ventilator-associated pneumonia from Gram staining and resistance records could reduce broad spectrum agents.

Patients scheduled for primary care appointments were more likely to get an influenza vaccine if they received a text message the night before indicating one was reserved for them, a new study shows.
Though many monoclonal antibodies were paused after demonstrated to be insufficient against the BA.1 Omicron subvariant, they may be more effective against BA.2.

A systematic review of clinical trials found a high probability that fluvoxamine prevented COVID-19 hospitalizations in outpatient settings.
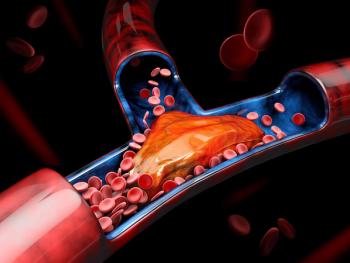
The risks of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and bleeding events were increased at 3 or more months after COVID-19 infection.
After the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) fully authorized the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, series-completing second doses increased substantially. However, first vaccine doses were actually administered at lower rates after the approval.
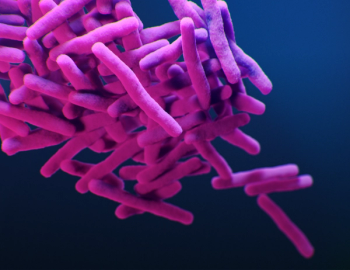
Bedaquiline-resistant tuberculosis is characterized in South Africa, where it has not been reserved as last resource for drug-resistant TB.

Being displaced by war is causing a disruption in treatment and long-term health care for Ukrainians. And it is likely, the situation will become more dire as the country’s public infrastructure worsens.








![What are Monoclonal Antibodies [mAb]? | John F. Kokai Kun, PhD](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/contagion/8b28909ccca26707c9ac984921b60d906bdd278c-750x424.png?w=320&fit=crop&auto=format)