At ID Week 2017, Dr. Laura Cooley, CDC, discussed the increasing number of Legionnaires’ cases in the United States, underscoring the need for stronger water management practices.

At ID Week 2017, Dr. Laura Cooley, CDC, discussed the increasing number of Legionnaires’ cases in the United States, underscoring the need for stronger water management practices.

Stay up-to-date on the latest infectious disease news by checking out our top 5 articles of the week.
Based on WHO guidelines for tuberculosis screening, many individuals who don’t have the disease are sent for expensive confirmatory testing. A simple point-of-care blood test could change all of that.

William Schaffner, MD, discusses how the adults aged 65 and older are disproportionately affected by influenza.

A multinational team of researchers set out to answer the following question when it comes to antiviral therapy for influenza: to combine or not to combine?

A new article details how researchers are working to develop a universal flu shot.
The pneumonic plague outbreak in Madagascar infects 684 individuals and claims 57 lives, thus far. Has it spread to Seychelles?

Pandemic influenza virus strains easily infect humans and spread from person-to-person in an efficient and sustained way. With no immunity to the novel virus and no vaccine to protect against it, what will the United States do?

Researchers in a pediatric hospital in Tokyo see positive results following the implementation of an antibiotic stewardship program limiting carbapenem use.

New tests continue to evolve that offer greater sensitivity than current methods.
Flu season has officially begun in the United States, as the first cases and deaths of the season are reported, prompting health officials to press for vaccination.

Prolonged antibiotic use opens the door to the development of antibiotic resistance, superinfections, and the risk of Clostridium difficile infections.

William Schaffner, MD, medical director for the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases’ (NFID), provides a brief overview of the past flu season (2016-2017).

New data reveal that when pregnant women receive the Tdap vaccine during pregnancy, it can prevent whooping cough in about 78% of newborns; however, only about 50% of pregnant women receive the vaccine.
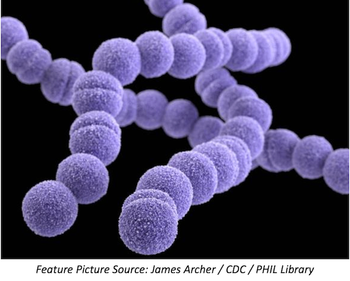
A new discovery about Group A Streptococcus may lead to the development of a new vaccine or antibiotic to prevent flesh-eating infections.
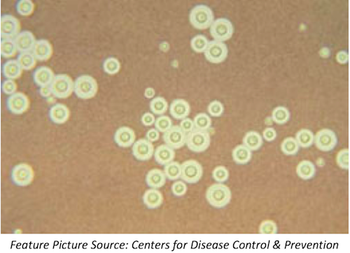
Death rates among HIV-positive patients diagnosed with cryptococcal meningitis were slightly lower when antiretroviral therapy was delayed a few weeks after diagnosis.

In case you missed them, we've compiled the top 5 articles from this past week.
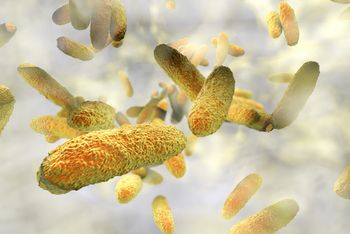
Following a deadly pneumonia outbreak in a Chinese hospital last year, researchers have identified a dangerous new superbug that is drug-resistant and highly virulent.

Alan Gross, PharmD, shares the drawbacks of some of the current prediction tools used for pneumonia.

WHO report confirms that “the world is running out of antibiotics” to treat resistant priority pathogens
Lefamulin, a pleuromutilin antibiotic, continues to meet primary endpoints for the treatment of community acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) in clinical trials.

Alex Rinehart, PhD, explains if cabotegravir interacts with any other medications.
Researchers from Imperial College in London have created a scoring system designed to predict 10-year tuberculosis (TB) risk in adult contacts of index cases.

As practitioners continue to mistake the worsening of asthma symptoms for bacterial respiratory infections, more antibiotics are being prescribed, many times, inappropriately.

Alan Gross, PharmD, shares how an early diagnosis of multidrug-resistant pneumonia can work towards improving patient outcomes.