Antibiotics
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Shionogi shared positive clinical cure rates from their ongoing trial of Fetroja (cefiderocol) for difficult-to-treat Gram-negative infections.

Extending antimicrobial stewardship programs to transition of care and discharge may prove beneficial to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use.
Novel β-lactamase inhibitor enmetazobactam with cefepime exceeded noninferiority to piperacillin/tazobactam in complicated UTI, pyelonephritis.
Oral antibiotics after partial completion of intravenous regimen for S aureus bacteremia improves outcomes of persons who inject drugs (PWID), which is a population that often has limited access to treatment.
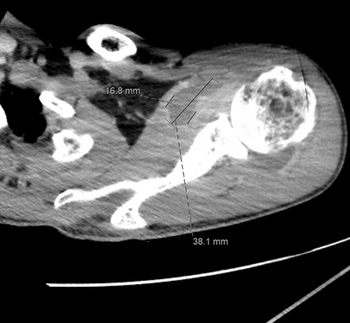
Gonococcal septic polyarthritis is an uncommon manifestation of N gonorrhoeae infection, but has increased by about 40% in recent years.

The limitation in the number of pediatric-specific guidelines by professional organizations, and results from large randomized clinical trials, may place an additional emphasis on literature evaluation skills for pediatric ASP pharmacists.

Recent issues surrounding the ADAPT-PO and SURE-2 trials place the spotlight on the difficulties developing oral carbapenem-based antibiotics and case their future into doubt.
Salmonella becomes more dangerous as antimicrobial resistance grows. Read about its most common manifestations.

Although there are challenges for clinical and infectious disease pharmacists when trying to apply this concept, here are some considerations and strategies to employ stewardship in this setting.

The Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee's (VRBPAC) positive vote follows the committee’s review of the data from the biologics license application (BLA) for RBX2660.
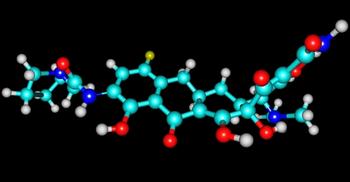
Eravacycline is an antibiotic that has been touted for possible treatment of difficult-to-treat resistant (DTR) Gram-negative infections. But can it tackle carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) infections?

The study authors identified four main approaches to antimicrobial stewardship programs after questionnaire and focus group discussions with ASP leaders.
Here is a review of using this therapy in this patient population.
Although hospitalizations due to urinary tract infections have increased, there are some investigational antibiotics in clinical trials. Here is a review of some of these therapies in the pipeline.

In the latest column from the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP), here is a discussion on the use of rifampin as an adjunctive antibiotic treatment for patients with diabetic foot osteomyelitis.

When physicians were told that a case was likely viral they were less likely to prescribe antibiotics, a new study shows.
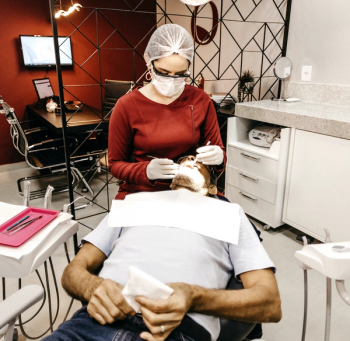
Dentists write about 25.7 million prescriptions annually, amounting to about 10% of all outpatient antibiotic prescriptions in the United States. A recent study showed that educating dentists about the risks of antibiotics—including antimicrobial resistance and Clostridioides difficile infections—led to sharp decreases in prescriptions.

Finding that the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted best antibiotic practices, the CDC announced further efforts to curb treatment-resistant infections.

With antimicrobial resistance a rising threat, the World Health Organization is working to heighten awareness of the urgent need for new therapies.
Here is a review of the literature for this class of antibiotics.

Investigators designed a quasi-experimental pre- and post-intervention analysis comparing a pre-intervention cohort receiving IV drip antibiotic infusion with a post-intervention cohort receiving IVP administration.

Working to Fight AMR is working in Washington DC to help pass policies in Congress to help alleviate this significant issue.

A robust stewardship program requires a comprehensive investment in technology and staff.
This agent is likely best utilized as part of a combination when treating this bacterium but data regarding appropriate combinations are scarce.