Zoonotic & Vector-Borne Diseases
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

According to the CDC, 28% of the Salmonella cases in this outbreak occurred in children under the age of 5 years.

Plague. West Nile Virus. Zoonotic influenza. What else made the CDC list of the top 8 zoonotic diseases of most concern in the US?

Triatoma sanguisugas, an insect also known as a “kissing bug,” can transmit the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which causes Chagas disease.

The FDA has approved the Dengvaxia vaccine for the prevention of dengue disease in children 9 to 16 years who have laboratory-confirmed previous dengue infection.
Johns Hopkins symposium will highlight new challenges and approaches in the fight against the mosquito-borne disease.

In a symposium at ECCMID 2019, Giovanni Rezza, MD, highlighted the growth of tropical outbreaks occurring in Europe and discussed how warmer temperatures may lead to more frequent tropical outbreaks.
Investigators used computer algorithms to predict primate species likely to be positive for Zika virus in Central and South America.

Contagion® is reflecting on the advancements in treatment and prevention that have been made in infectious diseases while identifying areas that need further improvement to reduce preventable deaths globally.
The CDC has released new guidance on the treatment for severe malaria following the manufacturing discontinuation of the only FDA approved IV antimalarial.

An analysis of spotted fever rickettsiosis epidemiology has found that only 1% of cases reported between 2010 and 2015 met the criteria for a confirmed case.

Deep-dives into Zika virus exposures shed light on how we can protect lab workers.

Solving a years-old mystery, investigators have discovered that MHC-II molecules can provide a gateway for bat influenza to infect human cells.

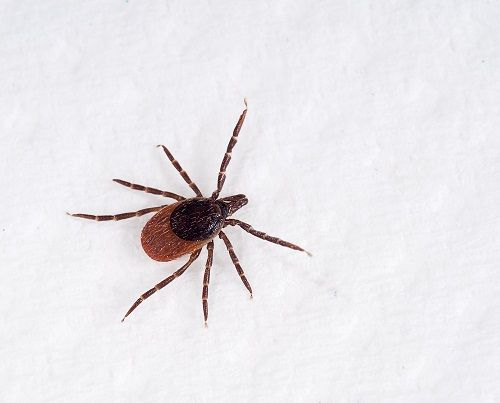
Powassan virus counts in the United States have been on the rise over the last decade, and now a new study sheds light on how ticks rapidly transmit the rare disease.
Rats and other pests pose significant problems for urban areas in the US.
As several Zika virus vaccine candidates undergo clinical trials, a group of investigators is taking an alternate approach to quell transmission by genetically engineering mosquitoes to be resistant to the virus.

The FDA has approved triclabendazole (Egaten) for the treatment of fascioliasis, a neglected tropical disease in patients 6 years of age and older
Single-dose tafenoquine shows promise for the radical cure of P vivax malaria, according to two new studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine.

Health officials announced that individuals who consumed raw milk from Miller’s Biodiversity Farm may have been exposed to a drug-resistant strain of brucellosis.
A new study reports that Zika antibodies persist for longer than initially believed, with antibodies detected in symptomatic patients 18 months after illness onset.

Rutgers University investigators created a pictorial key that anyone with a strong enough microscope can use to correctly identify the Asian longhorned tick from other harmless species.
TAK-003, being developed by Takeda, is a tetravalent vaccine based on a live-attenuated dengue serotype 2 virus, which provides the genetic “backbone” for all 4 virus serotypes.
Investigators followed a pediatric cohort in Nicaragua over the course of 15 years and found that dengue fever immunity offers some protection against symptomatic Zika disease.

Eleven cases of Salmonella Typhimurium have been reported in a multistate outbreak with a suspected link to contact with hedgehogs.
A new portable metagenomic technology allowed investigators to perform real-time analysis of viral genomes during a 2018 Lassa fever outbreak in Nigeria.
A new test can detect Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte carriers in saliva samples, providing a point-of-need rapid diagnostic test for malaria.