Zoonotic & Vector-Borne Diseases
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

At a media briefing this morning, Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) experts discussed the worldwide 600 confirmed cases of monkeypox.
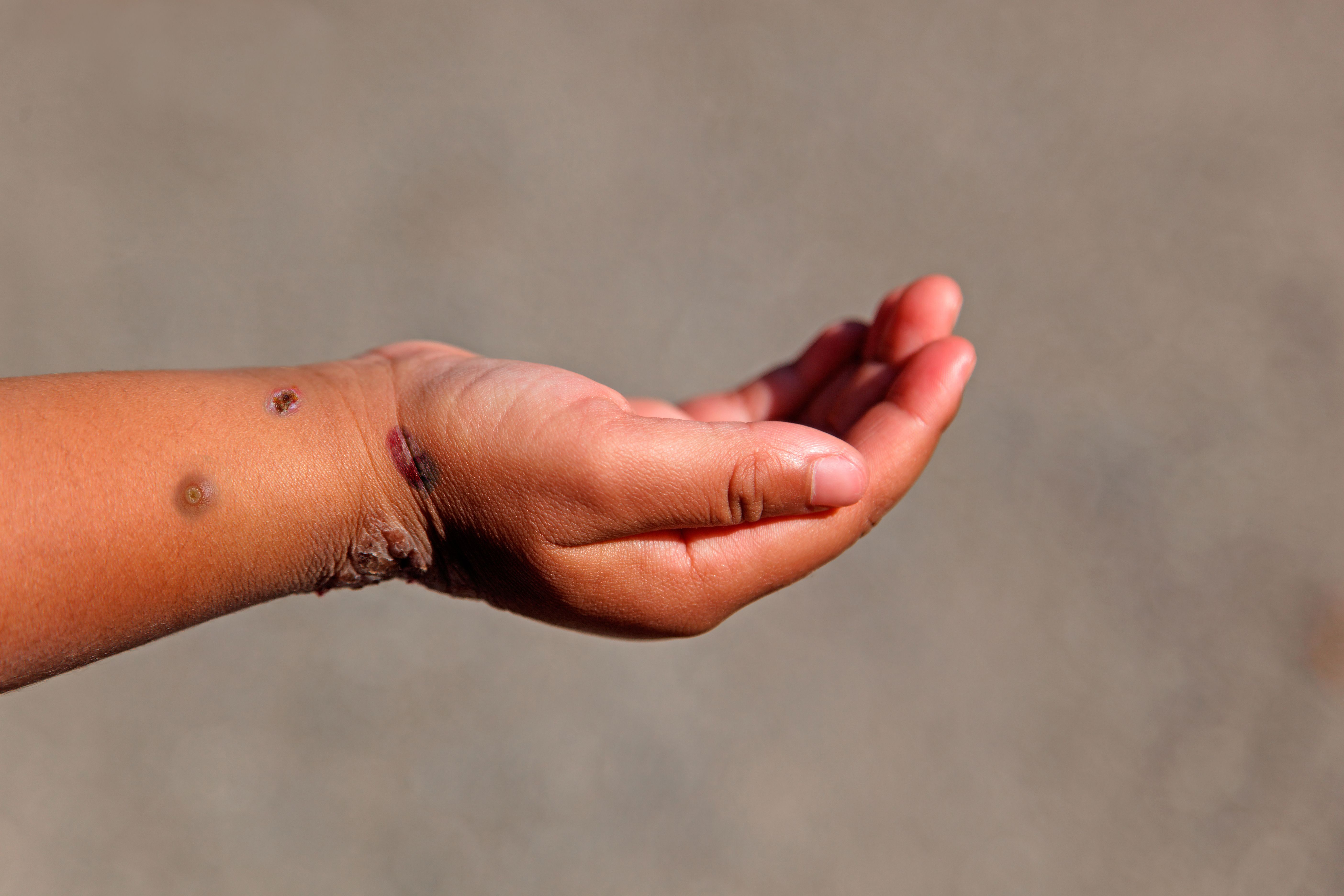
There are approximately 300 reported cases of monkeypox in about a dozen countries. However, Dr. Peter Hotez believes we are well equipped to prevent and treat the viral infection.
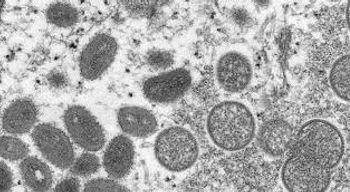
An expert cautions against panic but advises careful study and robust public health response.

New information suggests a few more cases have surfaced in the United States, pending CDC confirmation.


Research suggests a political disconnect on the status of global environment that could impact health response during a crisis.

Antibiotic-resistant strains of the dangerous superbug C difficile have been identified in pigs and humans, suggesting zoonotic transmission is possible.

Historically low incidence of dengue in southeast Asia and Latin America linked to COVID-19 restrictions suggests potential future interventions.

New models suggest that climate change will force animal populations to migrate, creating conditions for new viruses to emerge and jump to humans.

A Colorado person tested positive for avian influenza. The patient worked closely with poultry, their only symptom was fatigue, and they have since recovered after a few days.

Treating long-lasting nets with a new insecticidal combination that rendered mosquitos unable to fly reduced malaria infections in Tanzanian children by almost half.

Study of Heartland virus in lone star ticks in Georgia adds to evidence of how it evolves, spreads geographically, and causes disease.
A Tufts University research time identified a novel testing method to detect Lyme disease reinfection and successful treatment.

First-in-class triaminopyrimidine demonstrates antimalarial efficacy in first-in-human test of dosing, kinetics, and clearing parasite in infected volunteers.

There is no vaccine to prevent or treat chikungunya virus. Valneva announced 98.9% of phase 3 trial participants achieved CHIKV neutralizing antibodies after a signle dose of their vaccine candidate, VLA1553.

Pfizer’s TicoVac vaccine was developed to immunize young children and adults to prevent Tick-Borne Encephalitis.

A sub-analysis of phase 2 data compared the immunogenicity of their VLA15 vaccine in adults after administration of 2 or 3 primary series doses with the latter demonstrating a stronger response.

A study's results may have implications for future virus tracking.

Weekly Arakoda for malaria prevention was found safe and tolerable for healthy adults who travel internationally.

Analyzing the 100 largest zoonotic disease outbreaks, investigators found the most significant drivers to be water contamination, sewage management, weather conditions, and change in vector abundance.

Malaria has afflicted humanity for thousands of years, and the parasite is especially deadly for children and babies. The WHO has recommended the first malaria vaccine be deployed across sub-Saharan Africa.

One fatality of a 12-year old boy was reported in Kerala.

The STOP Spillover project is aiming to prevent remerging infectious disease outbreaks.

The National Institutes of Health (NIH) announces single injection of monoclonal antibody against the Plasmodium mosquito-borne parasite prevented malaria throughout 9 month phase 1 trial.

The company is planning to use its mRNA platform to develop the vaccine for malaria, which is the same successful technology it harnessed for its COVID-19 vaccine.