
As adults are living longer, they are able to continue to have healthy sex lives. Unfortunately, many are not practicing safe sex, and healthcare practitioners are not screening their older patients for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).

As adults are living longer, they are able to continue to have healthy sex lives. Unfortunately, many are not practicing safe sex, and healthcare practitioners are not screening their older patients for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Researchers uncover high rates of co-infections in patients who are admitted to hospitals with influenza.
A research team examines two Yosemite plague diagnoses to determine effectiveness of procedures for the detection, protection, and prevention of Yersinia pestis.
Researchers have found that anemia offers protection against malaria in African children and that iron supplements may actually reverse this protective effect.

Seeking to improve the nation’s health and safety, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has been targeting several high-burden issues in which it could make the greatest impact, and three such issues are infectious diseases.
Following superbug outbreaks around the world linked to contaminated endoscopic devices, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two new one-time use endoscopes.
A team of researchers has found that individuals with weakened immune systems are the most at risk of infection by listeriosis contamination in food products.
Sustaining a burn that lands a patient in the hospital may have long-term implications for their risk of acquiring infectious diseases later on.
A team from Duke University’s Developing World Healthcare Technologies Lab have discovered a way to extend the lifespan of antiretroviral drugs in order to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in developing countries.
An alternative treatment option for treating and preventing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia may be in the horizon for patients who cannot tolerate the standard therapy.
With cases of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea on the rise, researchers from the University of York may have made a breakthrough in the quest to find treatments that work.

New surveillance reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that this year’s influenza vaccine can offer effective protection against circulating viruses this flu season.

Derek Gatherer, PhD, lecturer at Lancaster University has compiled a list of emerging diseases to watch out for in 2017.

The year 2016 may be over, but the fight against the infectious disease that dominated headlines for most of the year—Zika virus—has only just begun.

Your cash is probably dirtier than you think, with the potential to serve as a vehicle for a number of harmful, disease-causing bacteria.
Research on a patient with acute myeloid leukemia has revealed new information on how bacteria mutate to survive antibiotics.

With the opening of a new R&D center in Rockville, MD, GlaxoSmithKline strives to improve global outbreak preparedness and calls for increased vaccine production capacity.
While more information on the Zika virus is revealed, researchers are saying that the United States can rest a little easier over concerns of a large-scale outbreak.
An emerging pharmaceutical company has partnered up with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to use its innovative technology to assist in the fight against HIV.
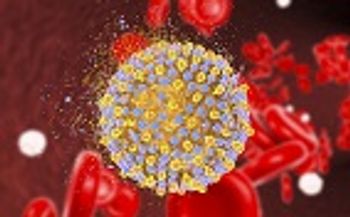
Despite the fact that an increasingly large portion of the hepatitis C (HCV)-infected population successfully achieves a cure for the infection, called sustained viral response (SVR), this population still deals with increased mortality rates.

A new coalition created by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and other global partners will launch at this year’s World Economic Forum, with the goal of supporting the fast-tracked development of new vaccines.
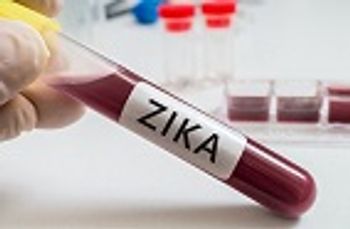
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health recommend integrating men into the family-planning process in the age of Zika.
A new study has revealed more information on how microbes confer resistance to antibiotics.
A new study takes a look at the efficacy of off-label treatments for Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection.

Harvoni has been added to Express Script’s formulary and will be available from the company’s Hepatitis Cure Value Program.
Low CD4/CDE8 ratio and a history of bacterial pneumonia heighten the risk for lung cancer in an HIV-positive population.


This year’s most-viewed article on ContagionLive combined two hot-button issues: social media and vaccination.
GlaxoSmithKline recently announced positive results from two recent trials of new antiretroviral drug regimens, showing HIV can be effectively treated with fewer medications.
A new study from University of Copenhagen researchers explains how some multidrug-resistant bacteria are able to survive lethal doses of antibiotics through a hibernation-like defense mechanism.