Gastrointestinal Infections
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
A new report finds veterans who took vitamin D supplements were less likely to get COVID-19 and less likely to die within 30 days of infection.

With major updates in HIV, C difficile, hepatitis, yeast infections, and skin and soft tissue infections, this week's Infectious Disease Update has something for everyone.
An easy-to-administer oral biologic kept repeat C difficile infections at bay in a new study.

The US FDA has accepted a Biologics License Application (BLA) for Seres Therapeutics' SER-109, and set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) action date of April 26, 2023.

Drs Abraham and Feuerstadt share recent data with emerging live biotherapeutic products, SER-109, CP101, and VE303, for treatment of recurrent C difficile infection (rCDI).

C diff patients live in fear of a recurrence, says gastroenterologist Paul Feuerstadt, MD. RBX2660 has entered the FDA pipeline and looks to end this vicious cycle.
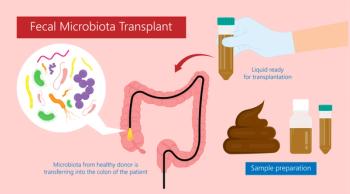
A fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) trial was halted early due to clear evidence the treatment was superior to placebo.

The incubation period of the original, wild-type COVID-19 strain was 6.65 days, while the Omicron variant's incubation period has shortened to 3.42 days.
Frequent recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection drives up financial burdens of the disease and underscores the need to improve access to treatment, infection prevention, and new therapies.
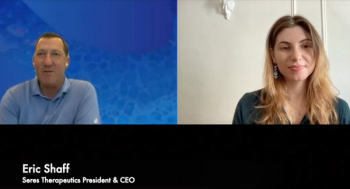
Eric Shaff, president and CEO of Seres Therapeutics, discusses the confirmatory trial findings for SER-109. Seres is filing a Biologics License Application for the recurrent C diff therapy.

SER-109, the investigational oral microbiome therapeutic from Seres, reduced C diff recurrence by 91.3% in at-risk populations.

Seres Therapeutics shared phase 3 trial results demonstrating their investigational microbiome-based therapeutic, SER-109, prevented recurrent C difficile infection (rCDI) in 88% of recipients.

Today, the FDA approved vonoprazan dual and triple therapies, developed by Phathom Pharmaceuticals to treat adults with H. pylori infection.

In a small retrospective study, 7 of 11 patients experienced clinical improvement.
Rising sea temperatures cause Vibrio species, bacteria linked to gastroenteritis, to be identified for the first time in UK waters.

Underweight elderly pneumonia patients were more likely to contract C difficile infection.
For the first time, investigators proved that a higher presence of Clostridioides difficile bacteria and toxins cause a more severe infection.

A global study of C. difficile isolates worldwide found a very high prevalence of the bacteria on shoe soles.
Rare cases of health care–associated meningitis and ventriculitis in adults caused by Candida species are associated with recent bacterial meningitis and broad-spectrum antibiotic use.
Investigators apply guidelines into practical management strategies.
An assessment of the frontline agents show similarities infection cure and recurrence rates at 30 days.
A meta-analysis suggest the 2 first-line C diff therapies provide similar outcomes, yet differ in recurrent infection risk.
A study shows countries with the highest income levels had greater vaccine protection against rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE).
Experts discuss the bacteria’s transmission in the community setting, how to reduce disease and economic burdens, and ways to improve quality of life for patients.