Gastrointestinal Infections
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Using enteral vancomycin for C diff prophylaxis may be the key to reducing morbidity and improving outcomes in pediatric and young adult recipients of HSCT.

Mark Riddle, MD, DrPH, speaks to Contagion at ACG 2019 about the results of a study looking into microbiome changes associated with single-dose antibiotics for the treatment of traveler's diarrhea.
Rebiotix has announced that it has completed enrollment of a phase 3 clinical trial for RBX2660.

Mark Riddle, MD, DrPH, speaks to Contagion about preventing drug resistance in people who acquire traveler's diarrhea.
Jab could save 600,000 lives, and hundreds of millions in health care costs.

DNA methyltransferase, an epigenetic process, has been found to mediate sporulation and pathogenesis in C diff.

Intravenous treatment of acute gastroenteritis can be costly and uncomfortable. A phase 3 clinical trial showed positive results for a bimodal release oral ondansetron tablet, finding the drug effective in treating nausea and vomiting.

RHB-105 (Talicia) is the only rifabutin-based therapy approved for the treatment of H pylori infection and is designed to address the high resistance of H pylori bacteria to current clarithromycin-based standard-of-care therapies.
RHB-105 is an “all-in-one” fixed-dose oral capsule comprising rifabutin 50 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg, and omeprazole 40 mg.
Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin more than doubled during the past 20 years, according to new research presented at UEG Week Barcelona 2019.

Natural disasters like hurricanes can have implications for public health, including a heightened risk of infectious diseases.
As outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases grow, it is important to review vaccination recommendations by age group.

Outbreaks of the water-borne pathogen increased an average of 13% each year between 2009 and 2017.

At MAD-ID 2019, Alison Lew, PharmD, spoke about her research on oral vancomycin prophylaxis to reduce CDI recurrence.
While young people with enteric infections have the lion’s share of symptoms, the elderly suffer higher rates of complications and hospitalizations from these illnesses. Arriving at a correct, timely diagnosis for this cohort of patients is key.
The FDA approved the vaccine in 2016 for adults between the ages of 18 and 64 who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Expanding the differential for diarrhea beyond Clostridium difficile.
A novel study from Seddon and colleagues adds to the body of evidence that supports what antimicrobial stewardship programs are so often challenged to do, early de-escalation.
Investigators at Johns Hopkins have developed a new saliva-based assay that would make norovirus infection testing less invasive.
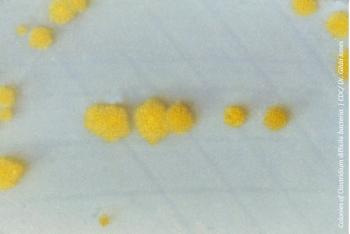
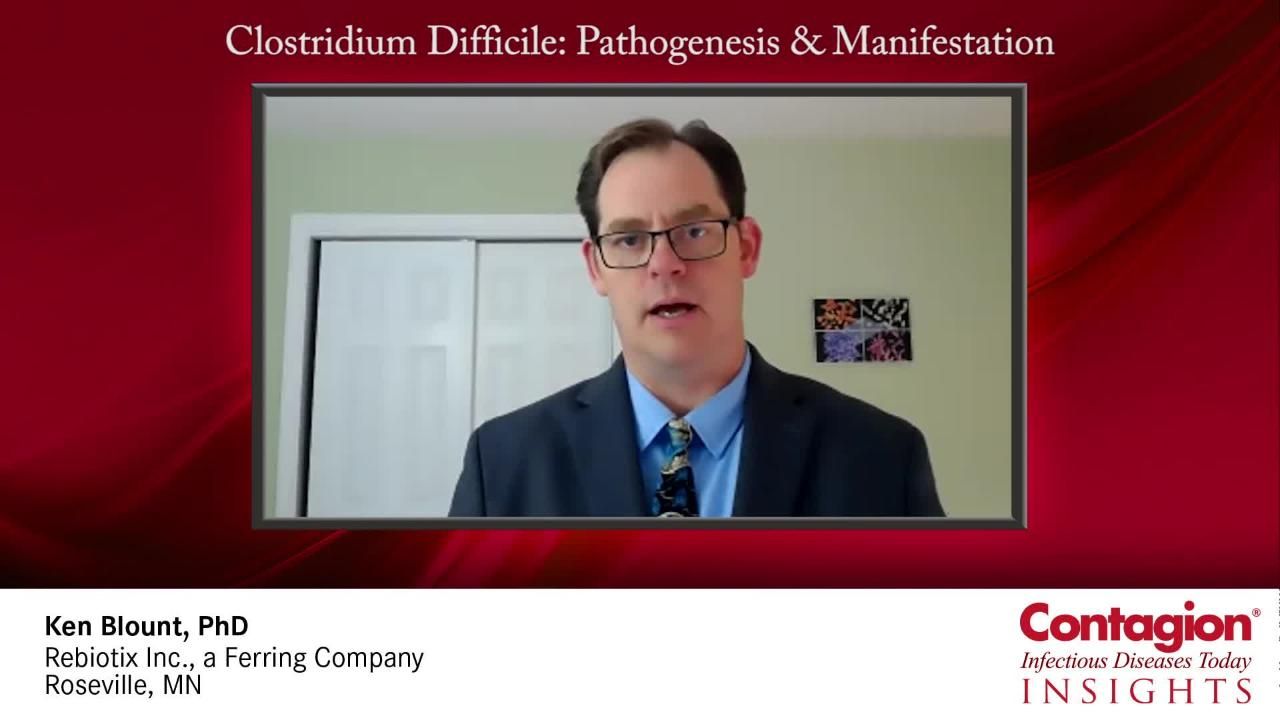
Nicola Petrosillo, MD, discusses current controversies in C difficile prevention and treatment.
A new study found that individuals who had low microbiota diversity prior to a bone marrow transplant were more likely to be at a higher risk for post-transplant complications.
Results from 2 new studies completed in the United States and Canada indicate that probiotic supplements do not produce any benefits for children with gastroenteritis.

Additionally, its use is associated with colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by lower relative quantities of some potentially protective bacterial organisms.

The FDA has approved the antibiotic for the treatment of adult patients with travelers’ diarrhea caused by noninvasive strains of E coli not complicated by fever or blood in the stool.

Glenn Tillotson, PhD discusses the development of new antibiotics and therapies for C diff during an era when antibiotic resistance is a serious global health threat.