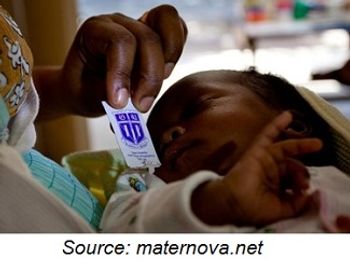
A team from Duke University’s Developing World Healthcare Technologies Lab have discovered a way to extend the lifespan of antiretroviral drugs in order to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in developing countries.

A team from Duke University’s Developing World Healthcare Technologies Lab have discovered a way to extend the lifespan of antiretroviral drugs in order to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in developing countries.
With cases of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea on the rise, researchers from the University of York may have made a breakthrough in the quest to find treatments that work.
An emerging pharmaceutical company has partnered up with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to use its innovative technology to assist in the fight against HIV.
Low CD4/CDE8 ratio and a history of bacterial pneumonia heighten the risk for lung cancer in an HIV-positive population.

GlaxoSmithKline recently announced positive results from two recent trials of new antiretroviral drug regimens, showing HIV can be effectively treated with fewer medications.

Experts suggest government efforts are sorely needed to provide education about HIV/AIDS to at-risk groups, especially among the young gay population.

Researchers from Australia may have found the key to the spread of antimicrobial-resistant gonorrhea in men who have sex with men (MSM).
A review of the top two video interviews from 2016 is included here.
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine researchers have found that genetic mutations of the NOD1 protein can result in increased risk of cytomegalovirus (CMV).

We’ve put together the top five biggest news stories on HIV Contagion covered this year. Did you read them all?
The 90-90-90 goal from the Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS has three prongs: By 2020, 90% of people with HIV worldwide will be aware of their status; 90% of HIV+ people will have access to treatment; and 90% of those with HIV will have a suppressed viral load. Money and training are key.
Researchers have found that current methods of predicting risk of heart attack or stroke in HIV-positive individuals are lacking.
The first large-scale clinical trial of a new HIV preventive drug, cabotegravir, has been launched and researchers are looking to see if it is just as effective as Truvada, the only licensed PrEP regimen currently available.
Although herpes remains one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections in the United States, the US Preventive Services Task Force is calling for less routine testing.
Researchers have found that commonly used antiretroviral drugs may be the cause of a number of cognitive problems.

Researchers from France recently found that higher base levels of vitamin D were not associated with a stronger immune response in HIV-infected patients.

Efforts to end the HIV/AIDS epidemic by 2030 face funding challenges, although new research is showing that we now have the tools and technology to eliminate the virus as a global health threat.
Researchers have found that the most common childhood cancer, acute lymphocytic leukemia, can be linked with congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV), a virus in the herpes family.

Researchers recently utilized Twitter user data to discern public opinions on the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine, with surprising results.
UC San Francisco researchers have found a link between pubic hair grooming and sexually transmitted diseases.
Acute myocardial infarction rates are higher in HIV-positive patients; a new study out of the VA may help clinicians determine who’s most at risk.

Male circumcision has been promoted by public health officials as a way of reducing HIV-1 infection rates, and now, the first study of its kind shows that circumcision rates have also impacted the spread of HIV-2 in West Africa.
As rates of syphilis have gone up around the world, a team of researchers from the University of Zurich have found that today’s epidemic strains have shared origins and emerged after the discovery of antibiotics.

A dynamic partnership has resulted in the development of a new, minimally-invasive device that can be used to treat HIV, cancer, and a number of other disease, ensuring medicinal adherence.